
Where is the location on Earth with the smallest gravitational value?
Answer, Layer 1: On the equator.
Let's sort out the thought process:
If the Earth were a homogeneous sphere that did not rotate and was not affected by other celestial bodies (like the moon), then theoretically, the gravitational acceleration at every point on the surface would be the same, with universal gravitation being considered as gravity.
But in reality, the Earth is constantly rotating. The further away from the axis of rotation, the greater the linear velocity. The linear velocity of an object at the equator is the greatest, and therefore, the centripetal force required is also the greatest, which is the "centrifugal force+" at its maximum, offsetting a part of gravity, thus the gravitational acceleration is naturally smaller.
Additionally, the Earth is not a perfect sphere; the radius near the equator is slightly larger than the polar radius. Therefore, the same object is further from the center of the Earth near the bulging equator than near the poles, and the universal gravitation it experiences is slightly smaller than in the polar regions (since the gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between objects when mass is constant). With a smaller universal gravitation and a larger "centripetal force," it becomes clear through force decomposition that gravity can only be smaller. Therefore, middle school geography teachers often tell students: for an object with a constant mass, the gravitational acceleration is the smallest at the equator.
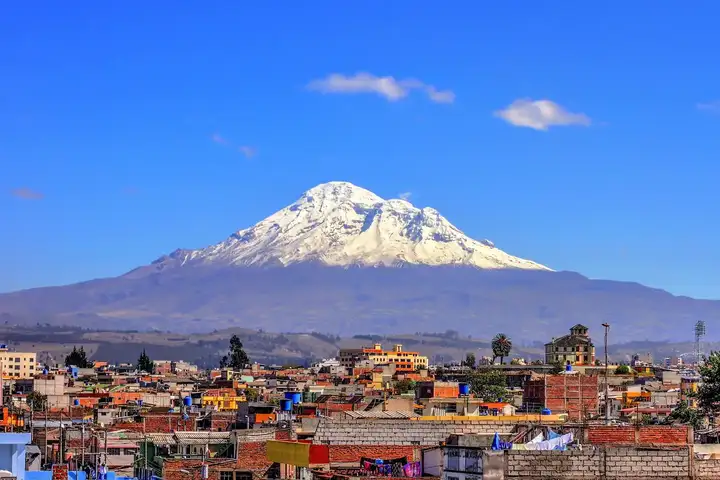

chimborazo
Answer, Layer 2: The summit near the equator.
If you are a middle school student, the first half of the first layer answer should be sufficient to deal with teachers and exams.
But the problem is that the real world is always more complex than theory.
The place on the Earth's surface farthest from the center is not Mount Everest, nor is it the equator, but the summit of Mount Chimborazo in central Ecuador, South America, at a height of 6,263.47 meters above sea level. A higher altitude means a greater distance from the center of the Earth, and gravity decreases with increasing altitude.
Additionally, considering the weak influence of the gravitational fields of the sun and moon, a mountaintop near the equator is a good alternative.
Therefore, the summit of Mount Chimborazo should be the place with the smallest surface gravitational acceleration, right?
Answer, Layer 3: The sea surface near the equator.
The previous discussion has a presupposition, which is that the Earth is an ideal sphere with a uniform density distribution, since the powerful effect of universal gravitation is created by the accumulation of mass.
However, the Earth is not spherically symmetric; the distribution of mass deep within it is uneven. The density of rocks under high mountains must be greater (like a compressed bun), and since water is lighter than rock, there is reason to guess that the density of rocks under the sea floor may be less than that under mountains at the same depth.
Prospectors and oil finders used this in the past, looking for local areas with abnormal gravity fields. The gravity field of a minefield is generally stronger, while the gravity field of sedimentary rocks is generally weaker relative to the surroundings.
Before the 21st century, humans had only measured some bodies of water near land. In 2002, NASA and the German Aerospace Center launched a satellite named GRACE, which observed more comprehensive changes in the Earth's gravity field in a near-polar low Earth orbit. Later, the gravity field was also measured several times with space shuttles [1, and in 2009, the GOCE satellite was launched +, which, in addition to onboard high-sensitivity gravimeters, also used GPS receivers to analyze the flight path to continuously track the subtle changes in the satellite with a precision of 2 to 3 centimeters [2].
The following image is a gravity field model based on GRACE data (not drawn to scale), with red representing areas with stronger gravitational acceleration and blue representing areas with weaker gravitational acceleration.

To view it conveniently, the Earth is flattened:

You will find that the large area with the lowest gravitational acceleration is located in the Indian Ocean southwest of Sri Lanka and near the equator in southern India [3. It even caused a depression in the sea level, where the sea level is 106 meters lower than the global average sea level!4. This gravity hole has a special name: the Indian Ocean Geoid Low (IOGL) [5]. As early as 1948, the Dutch geophysicist FelixAndries Vening Meinesz had already measured and discovered it during a voyage,
The reason for the existence of a gravity hole is speculated to be due to the collision of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate 20 million years ago, with low-density plate fragments continuously sinking into the seabed of the Tethys Ocean, and low-density magma from within the Earth (lava plumes) leaving these fragments near the IOGL, filling many lighter materials in the upper and middle mantle, thus causing uneven mass and density of the Earth. Of course, there are also some slightly different speculations [6].
Answer, Layer 4: The summit near the equator.
Researchers from around the world analyzed 3 billion (to be exact, 3,062,677,383) data points from multiple satellites (with a resolution of 250 meters), covering 80% of the Earth's land and 99.7% of the inhabited areas by population. Our home computers can calculate about 5 points per second, while supercomputers can complete the calculation of 3 billion points in three weeks!7.
The results show that the minimum gravitational acceleration on the equator is 9.7803, while the maximum is at the North Pole, at 9.83366.
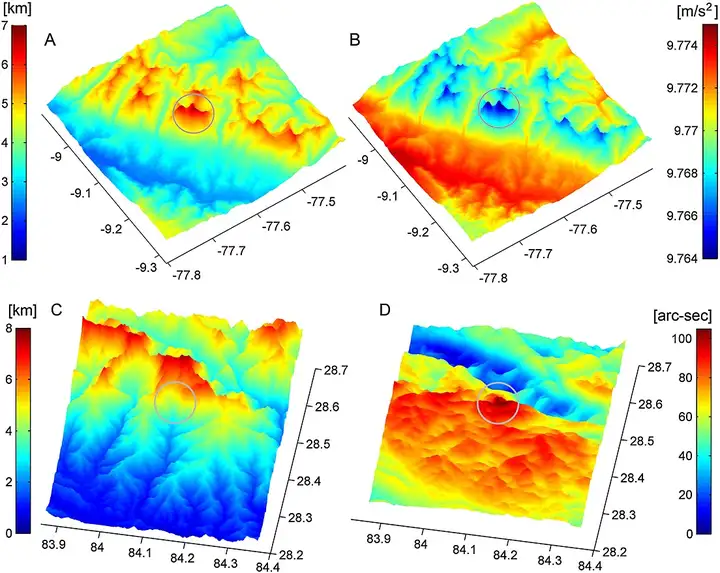
And the point with the lowest gravitational acceleration is surprisingly located in western South America, Peru, specifically on the summit of Mount Nevado Huascarán (at 9.12 degrees south latitude, 77.6 degrees west longitude). This mountain is located in the Huascarán National Park named after it (the highest altitude park in the tropics in the world) and is a section of the Andes Mountains. The gravitational acceleration there is only 9.76392[8].
After much ado, we're back to the mountaintop. Mount Huascarán can be considered the highest tropical peak in the world, with an altitude of 6,768 meters, slightly higher than Mount Chimborazo mentioned earlier (although it ranks fifth in South America).
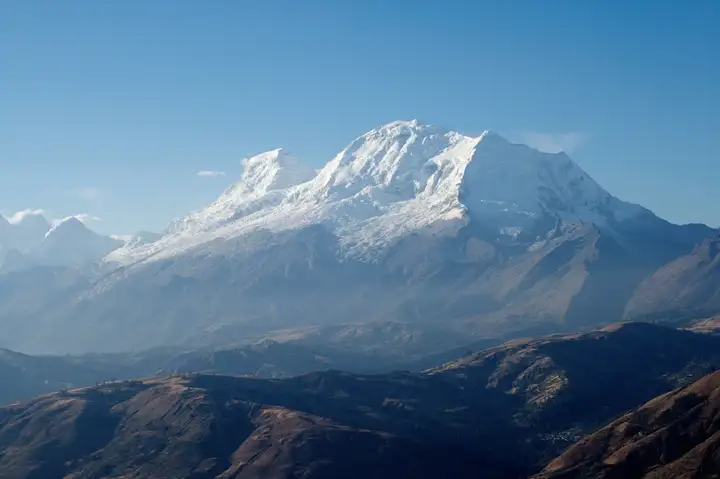

Mount Nevado Huascarán
You will find that the large area with the lowest gravitational acceleration is located in the Indian Ocean southwest of Sri Lanka and near the equator in southern India [3. It even caused a depression in the sea level, where the sea level is 106 meters lower than the global average sea level!4. This gravity hole has a special name: the Indian Ocean Geoid Low (IOGL) [5]. As early as 1948, the Dutch geophysicist FelixAndries Vening Meinesz had already measured and discovered it during a voyage,
The reason for the existence of a gravity hole is speculated to be due to the collision of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate 20 million years ago, with low-density plate fragments continuously sinking into the seabed of the Tethys Ocean, and low-density magma from within the Earth (lava plumes) leaving these fragments near the IOGL, filling many lighter materials in the upper and middle mantle, thus causing uneven mass and density of the Earth. Of course, there are also some slightly different speculations [6].
The following image is a comparison between Mount Huascarán and the Himalayan region, with the top row being Mount Huascarán and the bottom row being Annapurna Peak in Nepal (the 16th highest peak in the world) for comparison.
So the answer is:
The current minimum value of Earth's surface gravitational acceleration is not on the equator nor on the highest peak, Mount Everest, but on the summit of Mount Huascarán in Peru.
This means that when you travel from the North Pole to Mount Huascarán, without losing weight, your weight will decrease by about 1%, which is a weight loss of nearly 2 pounds for a 200-pound person (reading comprehension: why does the author here deliberately write the word "feel"? Is it the light flashing in the fish's eye?).
Or, if you accidentally fall into a 100-meter-deep hole, you will find that you will reach the bottom of the hole 16 milliseconds later on Mount Huascarán than at the North Pole.
Congratulations, your knowledge has increased.